How Zinc Supports Gut Health & Immune Function
Did you know that nearly 2 billion people worldwide don't get enough zinc in their diet? You're probably aware that zinc helps fight off colds, but its role in your body goes far deeper - literally. This essential mineral acts as a guardian for your gut health while simultaneously coordinating your immune system's response to threats. If you've been wondering why nutritionists keep emphasizing zinc's importance, you'll want to understand how this powerful mineral works to protect your wellbeing.
Key Takeaways
Zinc maintains intestinal barrier function by forming tight junctions between cells, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream.
The mineral activates immune cells and supports antibody production, strengthening the body's defense against pathogens and infections.
Zinc produces protective mucus for the gut lining while supporting the production of digestive enzymes and antimicrobial proteins.
Regular zinc intake helps repair and regenerate intestinal cells, maintaining a healthy gut environment and proper nutrient absorption.
Zinc deficiency can lead to compromised gut integrity, weakened immunity, digestive issues, and impaired nutrient absorption.
The Science Behind Zinc's Role in Gut Health
While many nutrients play important roles in digestive health, zinc stands out as an essential mineral for maintaining your gut's integrity. Your intestinal lining relies on zinc to form tight junctions between cells, preventing unwanted substances from leaking through.
These tight junctions act as selective barriers, allowing beneficial nutrients to pass while blocking harmful toxins and pathogens.
Zinc also supports your gut's immune function by helping produce digestive enzymes and maintaining proper stomach acid levels. It's vital for cell regeneration and repair of your intestinal lining, which constantly faces wear and tear.
Your body uses zinc to create new proteins needed for tissue healing and to regulate inflammation in your digestive tract. Without adequate zinc, you're more susceptible to digestive issues and compromised gut barrier function.
Understanding Zinc's Impact on Immune System Function
Zinc's role in gut health directly connects to its powerful effects on your immune system. When you maintain ideal zinc levels, you'll strengthen your body's defense mechanisms and enhance immune cell function.
Your gut barrier and immune system work together to protect you from harmful pathogens, and zinc plays a vital role in this partnership.
- Zinc activates T-cells and natural killer cells, which help fight off infections and viruses.
- It supports the production of antibodies that identify and neutralize harmful bacteria.
- Your body needs zinc to maintain the integrity of gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), where 70% of your immune system resides.
Without adequate zinc, your immune response can weaken, making you more susceptible to infections.
This mineral's dual action in supporting both gut health and immunity makes it essential for overall wellness.
Signs and Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
Recognizing zinc deficiency can be challenging since many symptoms overlap with other health conditions. You'll want to watch for both physical and cognitive signs that might indicate low zinc levels in your body.
| Physical Signs | Mental & Digestive Signs |
|---|---|
| Hair loss | Poor concentration |
| Slow wound healing | Reduced appetite |
| White spots on nails | Diarrhea |
| Skin problems | Brain fog |
| Frequent infections | Food doesn't taste right |
If you're experiencing several of these symptoms, don't self-diagnose. Instead, consult your healthcare provider for proper testing. They'll check your zinc levels through blood tests and evaluate other potential causes. The good news is that zinc deficiency is typically easy to correct through dietary changes or supplementation under medical supervision.
How Zinc Maintains Intestinal Barrier Function
To maintain a healthy gut barrier, zinc plays an essential role in strengthening the tight junctions between intestinal cells.
These junctions act as protective seals, preventing harmful substances from leaking through your intestinal wall into your bloodstream. When you're zinc-deficient, these barriers can become compromised, leading to increased intestinal permeability or "leaky gut."
- Zinc activates specific proteins that help form and repair tight junction complexes
- Your intestinal cells need zinc to produce protective mucus that shields the gut lining
- Zinc's antioxidant properties protect intestinal cells from inflammatory damage
Your gut's barrier function depends on adequate zinc levels to maintain its structural integrity.
This mineral helps your intestinal cells communicate effectively and supports the production of antimicrobial proteins that defend against harmful pathogens trying to breach your gut wall.
Dietary Sources of Zinc for Optimal Health
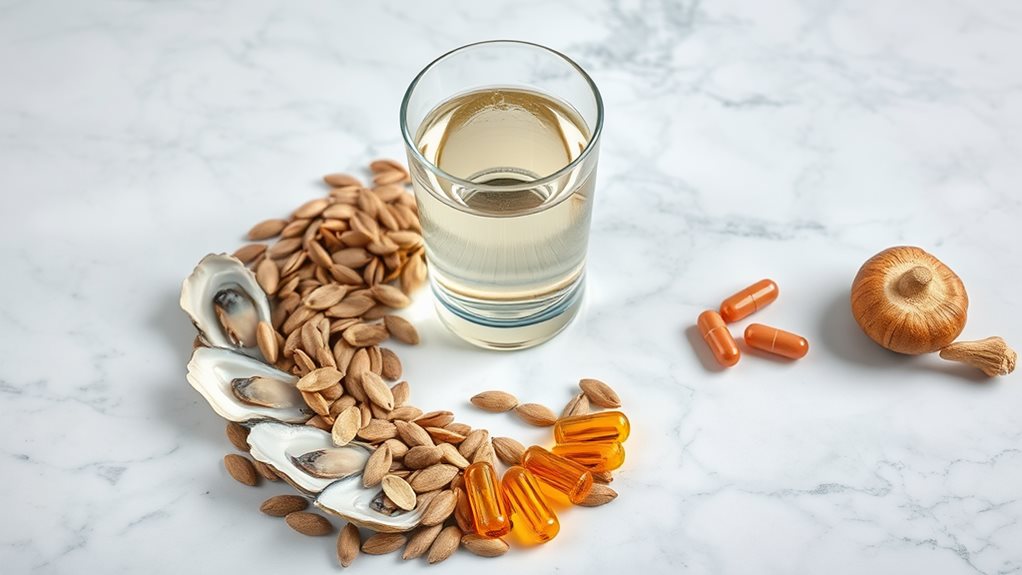
While many foods contain zinc, certain sources stand out as particularly rich in this essential mineral. You'll find the highest concentrations in oysters, beef, crab, and lobster.
Plant-based sources include pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, and lentils, though they're not as easily absorbed as animal sources.
To boost your zinc intake, incorporate grass-fed meat, shellfish, and legumes into your daily meals.
If you're vegetarian or vegan, you'll need to pay extra attention to your zinc consumption and might want to combine zinc-rich plants with vitamin C to enhance absorption.
Sprouting or soaking nuts, seeds, and legumes can also help reduce compounds that inhibit zinc absorption.
Remember that different cooking methods can affect zinc content, so it's best to use gentle cooking techniques when possible.
The Link Between Gut Microbiome and Zinc Status
As research advances in nutritional science, the intricate relationship between zinc and gut microbiota becomes increasingly clear. Your gut bacteria play a vital role in zinc absorption and metabolism, while zinc levels directly impact your microbiome's composition and diversity.
When you're zinc deficient, you'll likely experience changes in your gut barrier function and immune response.
- Zinc helps maintain the integrity of your intestinal wall, preventing harmful bacteria from entering your bloodstream.
- Adequate zinc levels support beneficial bacteria growth, particularly Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus species.
- Your gut bacteria can influence how efficiently you absorb zinc from food and supplements.
The two-way relationship between zinc and your gut microbiome highlights why maintaining proper zinc levels is essential for ideal digestive health and immune function.
Regular zinc intake through diet or supplementation can help keep this delicate balance in check.
Best Practices for Zinc Supplementation

Because zinc supplementation requires careful consideration, following proper guidelines guarantees you'll get the most benefit while avoiding potential side effects.
Take zinc supplements with food to minimize stomach discomfort, and choose forms like zinc picolinate or zinc citrate for better absorption. Don't exceed 40mg daily unless directed by your healthcare provider.
You'll want to separate zinc intake from iron supplements, calcium-rich foods, and certain medications by at least two hours, as these can interfere with absorption.
If you're taking antibiotics, wait until you've completed the course before starting zinc supplementation.
Monitor your zinc intake carefully if you're vegetarian or have digestive disorders, as you may need higher doses.
Regular blood tests can help confirm you're maintaining ideal zinc levels without oversupplementing.
Research-Backed Benefits of Zinc for Digestive Wellness
Scientific research has established zinc's powerful role in maintaining digestive health through multiple mechanisms. This essential mineral strengthens your intestinal barrier, helps repair damaged gut tissue, and supports the production of digestive enzymes vital for nutrient absorption.
Zinc deficiency can lead to increased intestinal permeability, often called "leaky gut," which may trigger inflammation and autoimmune responses.
Studies show that zinc helps maintain tight junction proteins in your gut wall, preventing harmful substances from entering your bloodstream.
Research confirms zinc's ability to regulate gut bacteria balance, promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms while inhibiting harmful pathogens.
Your body can't store zinc, so you'll need regular intake through diet or supplements to maintain these gut-protective benefits.
The mineral's ability to support both digestive and immune function makes it a cornerstone of gut health maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Zinc Supplements Interact With My Current Prescription Medications?
Yes, zinc supplements can interact with several prescription medications, so you'll need to be careful.
They may interfere with antibiotics, diuretics, and certain blood pressure medications.
Don't take zinc with penicillamine (used for rheumatoid arthritis) or bisphosphonates (for osteoporosis).
It's essential that you talk to your healthcare provider before starting zinc supplements to avoid any potential interactions with your current medications.
Does Zinc Absorption Change With Age or Certain Medical Conditions?
Did you know that up to 40% of older adults have insufficient zinc levels?
Your ability to absorb zinc does change as you age, with older adults typically absorbing less from their diet.
You'll also have reduced zinc absorption if you have conditions like Crohn's disease, celiac disease, or chronic diarrhea.
Certain medications and digestive disorders can impact your zinc levels too, so it's worth discussing your specific situation with your healthcare provider.
Is It Possible to Overdose on Zinc From Natural Food Sources?
It's very unlikely you'll overdose on zinc from food sources alone.
Your body has natural mechanisms to regulate zinc absorption from foods. However, you can get too much zinc from supplements.
The recommended daily allowance for adults is 8-11mg, and the upper limit is 40mg.
If you're eating a balanced diet with zinc-rich foods like meat, shellfish, and legumes, you won't exceed safe levels naturally.
How Long Does It Take to Correct a Zinc Deficiency?
The time to correct a zinc deficiency can vary based on your individual situation and the severity of your deficiency.
You'll typically start seeing improvements within a few weeks of proper supplementation or dietary changes. If you're taking zinc supplements, you'll want to follow your healthcare provider's recommended dosage.
Through a balanced diet rich in zinc sources like meat, shellfish, and legumes, you'll gradually restore your zinc levels over 2-3 months.
Can Zinc Supplements Be Taken During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding?
Perfectly planned pregnancy needs proper zinc!
You can take zinc supplements during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but you'll need to consult your healthcare provider first. They'll help determine the right dosage since your needs increase during these periods.
While zinc is vital for fetal development and milk production, don't exceed recommended amounts. Most prenatal vitamins already contain zinc, so you'll want to avoid double-dosing by checking your current supplements.
Conclusion
Studies show that nearly 2 billion people worldwide suffer from zinc deficiency, which can severely impact both gut and immune health. You'll want to guarantee adequate zinc intake through diet or supplementation to maintain your intestinal barrier function and robust immune response. Whether you're dealing with digestive issues or seeking to boost your immune system, zinc's role in your body's defense and gut health can't be overlooked.
Suggested next read: Why Do Older Men Need Joint Friendly Strength Training
